Geothermal Energy: A Sustainable Power Source?
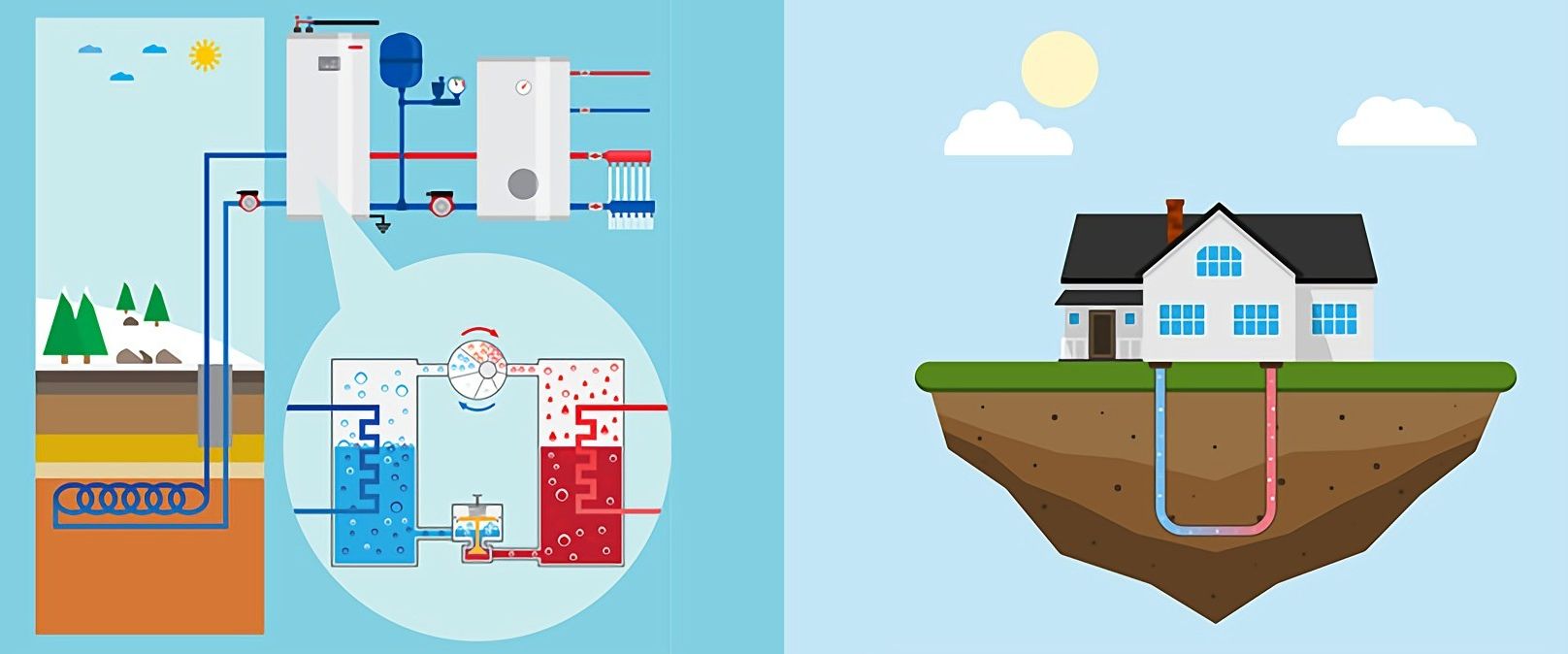
Geothermal energy, a renewable and sustainable power source, is harnessed by utilizing the Earth's internal heat. This heat, generated by the radioactive decay of minerals and the planet's formation, can be found in the form of hot water reservoirs, steam, and hot rocks deep within the Earth. By tapping into these resources, geothermal energy can generate electricity and provide heating and cooling through geothermal heat pumps.
Advantages of Geothermal Energy
1. Renewable and Sustainable:
Geothermal energy's primary advantage is its renewable and sustainable nature. Unlike fossil fuels, which are finite resources, the Earth's heat is essentially limitless, continually replenished by natural processes beneath the surface. This ensures a reliable and long-lasting energy source, minimizing environmental impact.
![Renewable geothermal energy source]
2. Low Carbon Footprint:
Geothermal energy boast a significantly lower carbon footprint compared to fossil fuels. Geothermal power plants produce minimal greenhouse gases, contributing positively to the fight against climate change. This makes them an environmentally friendly alternative to traditional energy sources.
3. Reduced Pollution:
Geothermal energy significantly reduces air and water pollution. Unlike fossil fuel power plants, geothermal plants do not burn fuels, eliminating harmful pollutants and particulate matter emissions. This promotes cleaner air and water, leading to improved public health and environmental well-being.
4. Stable and Predictable:
Unlike solar or wind energy, which rely on weather conditions, geothermal energy provides a stable and predictable supply of electricity and heating. This is particularly valuable for grid stability and ensuring consistent energy availability, even during peak demand periods.
5. Versatile Applications:
Beyond electricity generation, geothermal energy has diverse applications. Geothermal heat pumps can efficiently extract heat from the ground, providing efficient heating and cooling solutions for homes, buildings, and industrial processes. This versatility makes geothermal energy a valuable resource for various sectors.
Disadvantages of Geothermal Energy
1. High Initial Costs:
Developing geothermal projects comes with substantial upfront costs. Drilling deep into the Earth and constructing geothermal power plants requires significant investments. Exploratory drilling to identify suitable geothermal reservoirs further increases expenses. This can make geothermal projects less competitive compared to other renewable energy sources.
2. Limited Geographical Availability:
Geothermal energy's availability depends on suitable geothermal reservoirs, which are limited to specific geological settings. This restricts large-scale geothermal development to areas with favorable geology, limiting its widespread adoption in other regions.
3. Potential for Land Subsidence:
Extracting geothermal resources can lead to land subsidence, causing the Earth's surface to sink. This occurs when fluids are extracted faster than their natural recharge rate. Land subsidence can damage infrastructure, including buildings and roads, and disrupt natural ecosystems. Careful reservoir management and monitoring are crucial to mitigate this risk.
4. Release of Harmful Substances and Radon Gas:
While considered environmentally friendly, concerns exist regarding the release of harmful substances from geothermal fluids. These fluids can contain trace amounts of toxic elements like mercury, arsenic, and sulfides. Proper treatment and control are essential to prevent environmental and public health risks. Additionally, some geothermal areas release radon gas, which can be harmful in high concentrations.
5. Extensive Exploration Required:
Geothermal projects require comprehensive assessments and exploratory drilling before development. This exploration phase can be time-consuming and expensive, with the risk of not finding sufficient resources to support a commercial operation.
Conclusion
Geothermal energy presents a promising renewable energy solution with numerous advantages, including its sustainability, low carbon footprint, versatility, and stable energy supply. However, challenges exist, such as high initial costs, limited geographical accessibility, potential land subsidence, and the release of harmful substances. Extensive exploration is also required before project development. Despite these challenges, geothermal energy offers a significant contribution to a cleaner and more sustainable future.
For more information, check out the following resources: